A Comprehensive Comparison and Application Guide
In metal surface corrosion protection, electroplating and hot-dip galvanizing are two common techniques. They both apply a zinc coating to the surface of metals to enhance their corrosion resistance. While their end results may seem similar, these two methods differ significantly in terms of the process, durability, and suitable applications.
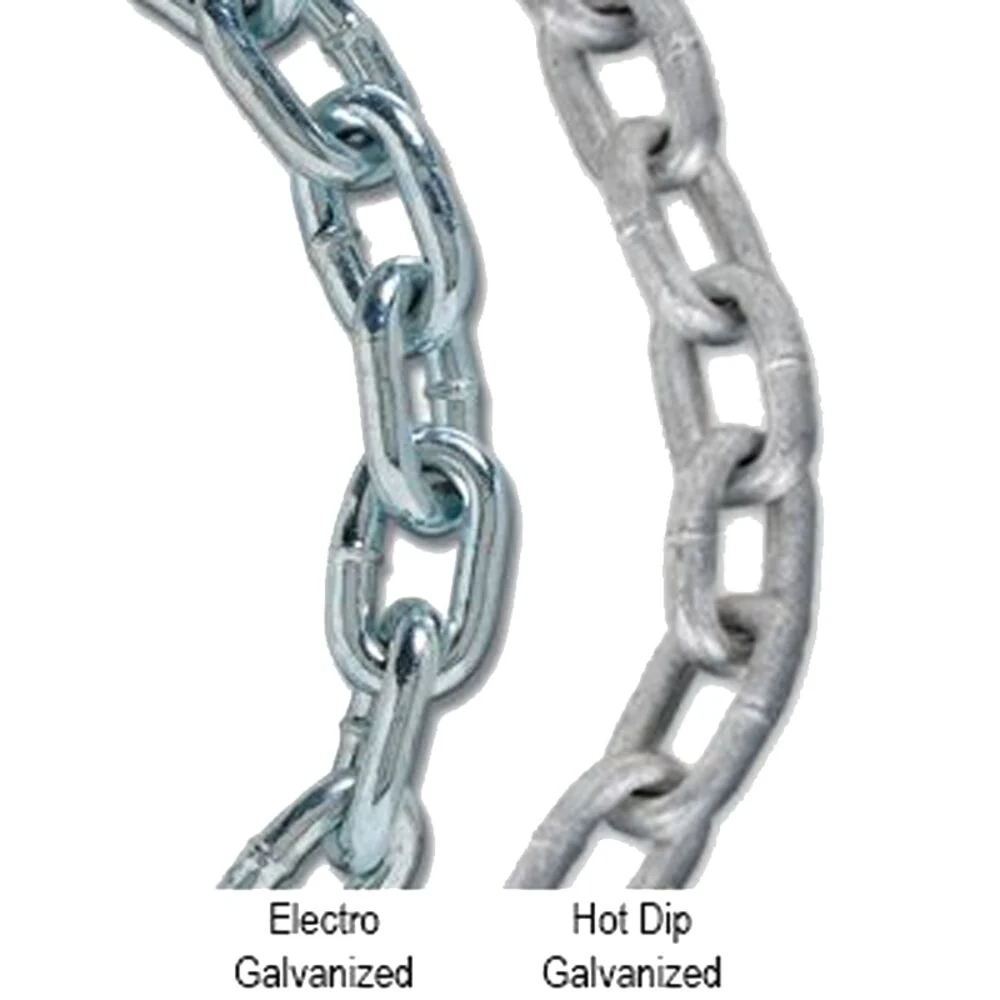
Hot-Dip Galvanized chain
- Process: The chain is fully submerged in a bath of molten zinc, creating a thick, fused zinc coating.
- Corrosion Resistance: Offers excellent long-term protection against rust and corrosion, even in harsh environments.
- Appearance: Typically has a dull, gray finish.
- Applications: Ideal for outdoor applications, structural components, and situations where long-term durability is crucial.
- Durability: Known for its high strength and resistance to damage.
- Maintenance: The zinc layer can self-repair through electrochemical reactions when damaged.
- Lifecycle: A long-lasting coating, with a lifespan averaging 20 to 50 years.
Electroplated Zinc Chain
- Process: The chain is placed in an electrically charged solution of zinc and saline, where the zinc is deposited onto the steel.
- Corrosion Resistance: Provides good protection against corrosion, but is less durable than hot-dip galvanizing.
- Appearance: Has a shiny, smooth finish.
- Applications: Suitable for indoor, dry environments, and where a more aesthetic finish is desired, like furniture, hardware, or decorative chains.
- Durability: The thin zinc layer is less resistant to damage than hot-dip galvanizing.
- Maintenance: The zinc layer is less resistant to damage than hot-dip galvanizing.
- Lifecycle: A shorter-lasting coating than hot-dip galvanizing.
Key Differences Summarized:

| Feature | Hot-Dip Galvanized | Electric Galvanized (Zinc Plated) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Immersion in molten zinc | Electroplating (using an electrical current) |
| Zinc Coating | Thick, fused zinc layer | Thin, shiny zinc layer |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, long-term protection | Good, but less durable than hot-dip |
| Appearance | Dull, gray finish | Shiny, smooth finish |
| Applications | Outdoor, structural, heavy-duty applications | Indoor, dry environments, decorative applications, and applications where a smooth finish is desired |
| Durability | High strength, resistant to damage | Less durable, prone to damage |
| Lifespan | Average of 20-50 years | Shorter lifespan than hot-dip galvanizing |
Which One is Right for Your Needs?
Choosing between electroplated zinc and hot-dip galvanizing depends on your specific requirements:
- For small parts or items that require a polished appearance and light corrosion protection, electroplated zinc is ideal. It is commonly used for household appliances, decorative products, and other small parts.
- For large structures, construction materials, and outdoor applications exposed to harsh environments, hot-dip galvanizing is the preferred choice. It provides a thicker coating with superior corrosion resistance.
If you’re unsure which coating is right for your application or need expert advice, contact us today. Our team can guide you through the selection process and ensure your project gets the corrosion protection it deserves.