Eye Bolts and Eye Nuts: Understanding Their Differences, Applications, and Installation
- Eye Bolts and Eye Nuts: Understanding Their Differences, Applications, and Installation
- What Are Eye Bolts and Eye Nuts?
- Common Applications of Eye Bolts and Eye Nuts
- How Many Types of Material For Eye bolts and Eye nuts?
- Installing Eye Bolts and Eye Nuts
- How to maintain and store eye bolts and eye nuts?
- What are the standards for eye bolts and eye nuts?
- Conclusion
Eye bolts and eye nuts are essential fasteners for lifting, load securing, and mechanical assembly. While similar, they serve different purposes. This guide explains their distinctions, applications, and proper installation for safety and efficiency.
What Are Eye Bolts and Eye Nuts?
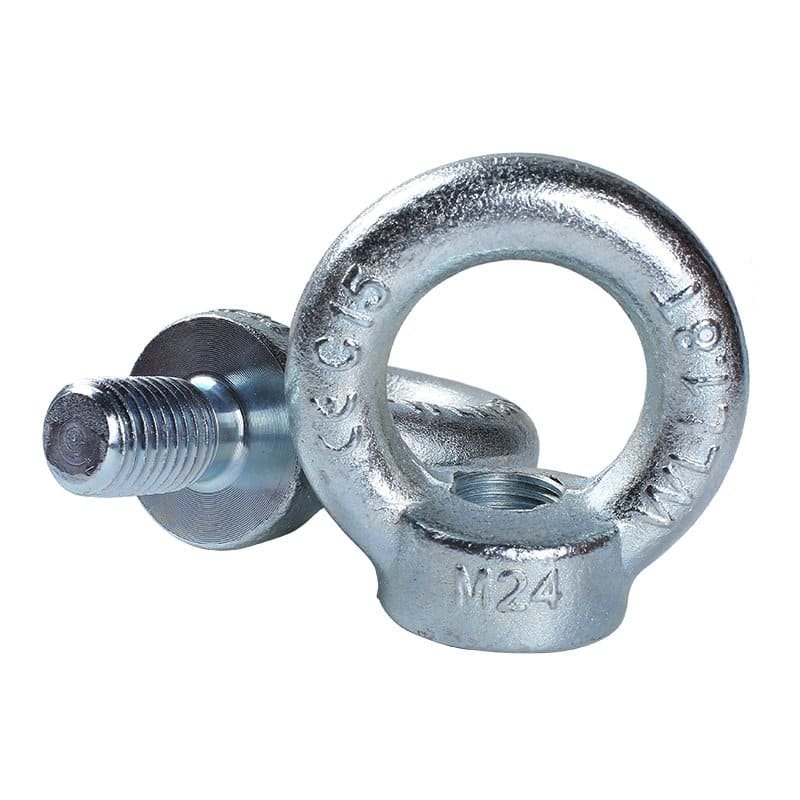

Eye Bolts: These are bolts with a loop (or “eye”) at one end and threads at the other. Eye bolts are used for attaching or securing items to a load, making them essential for lifting applications.
Eye Nuts: Eye nuts, on the other hand, are nuts with a loop at the top and internal threads. They are typically used in conjunction with bolts or threaded rods. Eye nuts are commonly employed in applications where the bolt needs to be screwed into the fastener securely.
Common Applications of Eye Bolts and Eye Nuts
| Application | Eye Bolts | Eye Nuts |
|---|---|---|
| Lifting & Hoisting | Used with cranes, hoists, and forklifts to lift heavy loads. | Also used in lifting, but often paired with threaded rods or bolts for adjustable rigging. |
| Securing Equipment | Anchored into structures to hold machinery, cables, or fixtures. | Attached to threaded rods or bolts to stabilize equipment in place. |
| Tie-Down Applications | Less common for tie-downs due to fixed installation. | Frequently used in cargo transport, automotive, and shipping to secure loads. |
How Many Types of Material For Eye bolts and Eye nuts?
Do you know how many materials of eye bolts and eye nuts? Different materials have different performance.
| Material | Pros | Cons | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | – Low cost, economical – High strength for general loads – Can be galvanized for corrosion resistance | – Prone to rust if untreated – Heavier than stainless steel | Indoor equipment, general lifting |
| Stainless Steel (304/316) | – Excellent corrosion resistance – No coating needed, low maintenance – Moderate strength | – More expensive than carbon steel – 316 has slightly lower strength than alloy steel | Marine, chemical plants, and outdoor use |
| Alloy Steel (Grade 8/10) | – Ultra-high strength for heavy loads – Heat-treated for durability | – Requires anti-corrosion coating – Expensive and heavy | Heavy machinery, mining, and dynamic lifting |
| Brass | – Corrosion-resistant (especially in seawater) – Non-magnetic, decorative – Lightweight | – Low strength, not for heavy loads – Higher cost | Marine decor, electrical/medical equipment |
Installing Eye Bolts and Eye Nuts
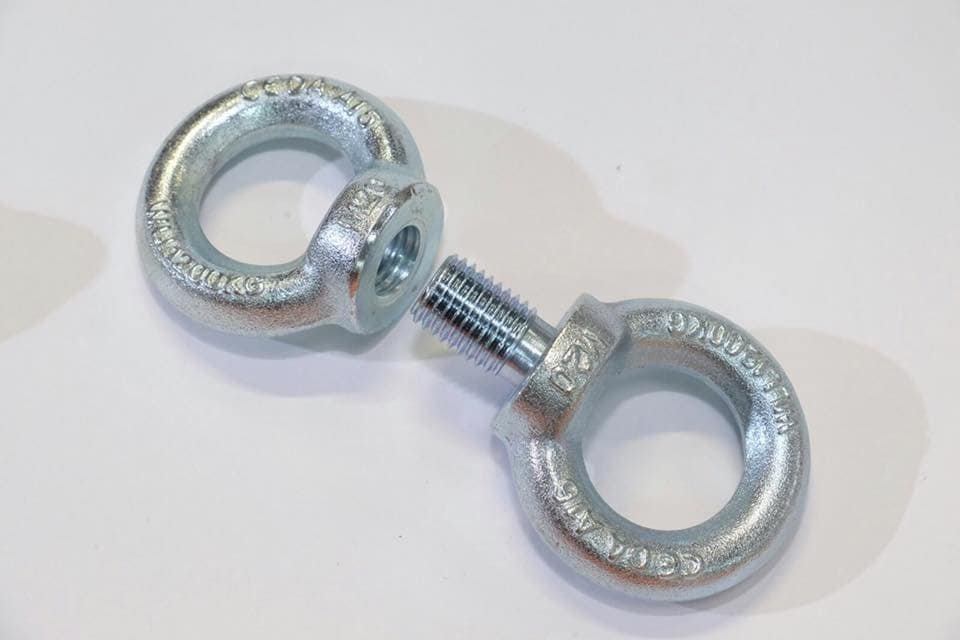

Proper installation is crucial to ensure the safety and stability of your setup.
- Inspect the eye bolt for cracks, bends, or rust before use.
- Prepare the mounting surface – it must be clean, flat, and strong enough.
- Match the threads exactly to the hole or nut.
It’s important to not overtighten, as this can lead to unnecessary stress on the material.
Torque & Tightening Force
| Material | Recommended Torque (for M10 example) | Critical Note |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | 25–30 Nm | Use a thread locker if vibration is expected. |
| Stainless Steel | 20–25 Nm | Higher risk of galling—lubricate threads. |
| Alloy Steel | 30–35 Nm | Never exceed the manufacturer’s specs. |
Angle load capacity comparison table
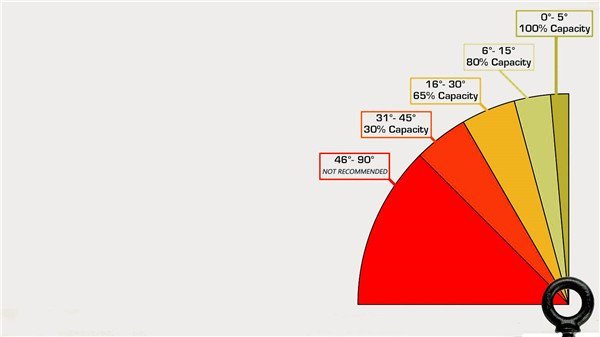
| Load Angle | Load Capacity (% of Vertical) | Safety Level | Operating Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0° | 100% | Safe | Optimal loading direction can be used at full capacity |
| 30° | 85%~90% | Safe | Permitted use requires regular inspection |
| 45° | 70%~80% | Caution | Reduce the working load, avoid prolonged use |
| 60° | 50%~60% | Danger | Emergency use only, strictly prohibit frequent use |
| 80°-90° | ≤50% | Prohibited | Absolutely no side loading! May fail instantly |
How to maintain and store eye bolts and eye nuts?
To ensure their performance and safety over a long period of use, regular maintenance and care are essential.
Regular Inspection: Check eye bolts and eye nuts for wear, corrosion, or cracks regularly, and ensure the load label is clear.
Cleaning: Keep them clean to prevent dirt or grease buildup, especially on the threads. Use mild cleaners and avoid harsh chemicals.
Lubrication: Apply lubricating oil to the threads regularly to reduce friction and wear, ensuring smooth operation.
Inspection and Replacement: Check for worn threads and ensure there is no damage. Replace damaged components promptly.
Avoid Overloading: Ensure the eye bolts and eye nuts do not exceed their rated load capacity. Regularly verify the load limit.
Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, well-ventilated area, avoiding humid or corrosive environments.
Record and Log Checks: Keep a log of regular inspections and maintenance to track the equipment’s condition and ensure safe use.
Regular inspection and maintenance will extend the lifespan of eye bolts and eye nuts, minimizing safety risks.
What are the standards for eye bolts and eye nuts?
Eye bolt and eye nut standards and certifications mainly come from organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), and the German Institute for Standardization (DIN). The following are some common standards and certifications:
ISO 3134 AND ISO 5922
ASTM A489 AND ASTM F1145
DIN 580 AND DIN 582
BS 4278 AND BS 580
EN 1677
JIS B 1174
Conclusion
Eye bolts and eye nuts are versatile, essential components in a variety of industrial and commercial applications. Choose the right type, material, and install correctly to ensure secure lifting and fastening in industrial applications. Critical for safety and performance.


