Wire Rope Clips FAQ: Everything You Need to Know
- Wire Rope Clips FAQ: Everything You Need to Know
- What is a wire rope clip?
- What are the most commonly used types of wire rope clips?
- How do I choose the correct size of a wire rope clip?
- What are the spacing and torque requirements when installing wire rope clips?
- What is the correct way to install wire rope clips?
- What’s the difference between forged and malleable wire rope clips?
- How often should I inspect wire rope clips?
- Can wire rope clips be reused?
- Are there alternatives to wire rope clips?
- How long should the dead end be when using wire rope clips?
Wire rope clips may seem like small components, but they play a critical role in securing wire rope assemblies across a wide range of industries—from construction and shipping to lifting and rigging. Whether you’re a first-time user or a seasoned professional, questions often arise about proper sizing, installation, and safety practices.
In this FAQ guide, we’ve compiled answers to the most frequently asked questions about wire rope clips. From choosing the right type to avoiding common installation mistakes, this post will help you use wire rope clips safely and effectively.
What is a wire rope clip?

A wire rope clip, also known as a cable clamp or wire rope clamp, is a mechanical device used to secure the loose end of a wire rope back to the main length (the “live end”). It’s commonly used to form a loop or eye in the wire rope, often for temporary or adjustable rigging purposes.
What are the most commonly used types of wire rope clips?
There are some main types of wire rope clips commonly used in rigging and cable assembly applications
DIN741 standard wire rope clip

It is one of the most widely used types of wire rope clips in Europe for light to medium-duty applications.
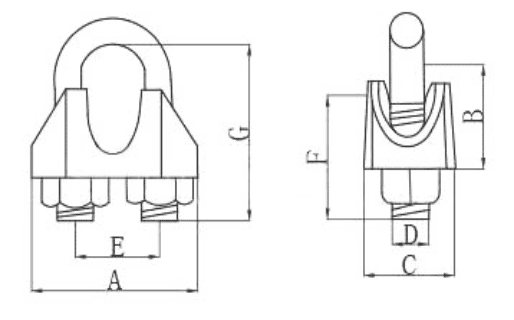
| Size | Diemension(mm) | Weight | ||||||
| mm | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | 100pcs(lbs) |
| 3 | 21 | 10 | 10 | 4 | 9 | 12 | 16.6 | 3.09 |
| 5 | 23 | 10 | 11 | 5 | 11 | 13 | 19.65 | 3.3 |
| 6.5 | 26 | 11 | 12 | 5 | 13 | 15 | 23.65 | 4.63 |
| 8 | 30 | 15 | 14 | 6 | 16 | 19 | 28.85 | 9.04 |
| 10 | 34 | 17 | 18 | 8 | 19 | 22 | 35 | 15 |
| 11 | 36 | 18 | 19 | 8 | 20 | 22 | 37 | 15.87 |
| 13 | 40 | 21 | 23 | 10 | 24 | 30 | 46.24 | 28.7 |
| 14 | 44 | 22 | 23 | 10 | 25 | 30 | 48.24 | 29.76 |
| 16 | 50 | 26 | 26 | 12 | 29 | 33 | 52.5 | 46.3 |
| 19 | 54 | 30 | 29 | 12 | 32 | 38 | 64.5 | 61.7 |
| 22 | 61 | 34 | 33 | 14 | 37 | 44 | 72.5 | 88.2 |
| 26 | 65 | 37 | 35 | 14 | 41 | 45 | 82.5 | 97 |
| 30 | 74 | 43 | 37 | 16 | 48 | 50 | 95.6 | 145.5 |
| 34 | 80 | 50 | 42 | 16 | 52 | 55 | 105.6 | 187.4 |
| 40 | 88 | 55 | 45 | 16 | 58 | 60 | 125.6 | 229.3 |
DIN1142 wire rope clip
DIN 1142 wire rope clip is a heavy-duty cable clamp standardized by the German DIN system, designed for higher strength and safer performance than the DIN 741 type. It is commonly used in industrial rigging, lifting, and load-bearing applications.
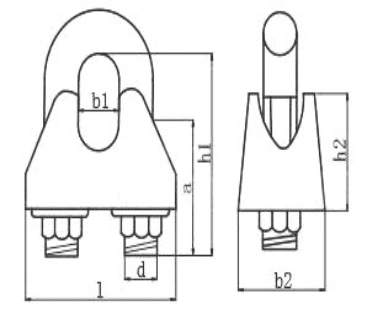
| Size | Diemension(mm) | Weight | ||||||
| mm | a | b1 | b2 | d | h1 | h2 | l | 100pcs(lbs) |
| 5 | 13 | 7 | 13 | 5 | 25 | 13 | 25 | 5 |
| 6.5 | 17 | 8 | 16 | 6 | 32 | 14 | 30 | 9 |
| 8 | 20 | 10 | 20 | 8 | 41 | 18 | 39 | 18 |
| 10 | 24 | 12 | 20 | 8 | 46 | 21 | 40 | 20 |
| 13 | 30 | 15 | 28 | 12 | 64 | 29 | 55 | 61 |
| 16 | 35 | 18 | 32 | 14 | 76 | 35 | 64 | 95 |
| 19 | 36 | 22 | 32 | 14 | 83 | 40 | 68 | 108 |
| 22 | 40 | 24 | 34 | 16 | 96 | 44 | 74 | 150 |
| 26 | 50 | 26 | 38 | 20 | 111 | 51 | 84 | 258 |
| 30 | 55 | 34 | 41 | 20 | 127 | 59 | 95 | 309 |
| 34 | 60 | 38 | 45 | 22 | 141 | 67 | 105 | 470 |
| 40 | 65 | 44 | 49 | 24 | 159 | 77 | 117 | 591 |
G450 wire rope clip
The G-450 wire rope clip, also known as a U.S. type drop forged wire rope clip, is a high-strength cable clamp designed for critical rigging and lifting applications. It is widely used in North America and internationally in environments where safety and load-bearing capacity are essential.
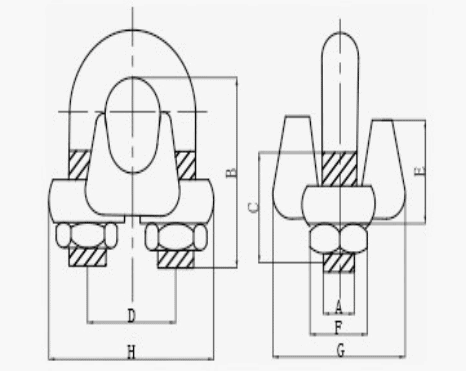
| Size | Diemension(mm) | weight | |||||||
| in | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | 100pcs(lbs) |
| 1/8 | 0.22 | 0.72 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.81 | 0.99 | 6 |
| 3/16 | 0.25 | 0.97 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.5 | 0.44 | 0.94 | 1.18 | 10 |
| 1/4 | 0.31 | 1.03 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.66 | 0.56 | 1.19 | 1.43 | 19 |
| 5/16 | 0.38 | 1.38 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 1.31 | 1.66 | 28 |
| 3/8 | 0.44 | 1.5 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.91 | 0.75 | 1.63 | 1.94 | 48 |
| 7/16 | 0.5 | 1.88 | 1 | 1.19 | 1.13 | 0.88 | 1.91 | 2.28 | 78 |
| 1/2 | 0.5 | 1.88 | 1 | 1.19 | 1.13 | 0.88 | 1.91 | 2.28 | 80 |
| 9/16 | 0.56 | 2.25 | 1.25 | 1.31 | 1.34 | 0.94 | 2.06 | 2.5 | 109 |
| 5/8 | 0.56 | 2.25 | 1.25 | 1.31 | 1.34 | 0.94 | 2.06 | 2.5 | 110 |
| 3/4 | 0.62 | 2.75 | 1.44 | 1.5 | 1.39 | 1.06 | 2.25 | 2.84 | 142 |
| 7/8 | 0.75 | 3.12 | 1.62 | 1.75 | 1.58 | 1.25 | 2.44 | 2.16 | 212 |
| 1 | 0.75 | 3.5 | 1.81 | 1.88 | 1.77 | 1.25 | 2.63 | 3.47 | 252 |
| 1-1/8 | 0.75 | 3.88 | 2 | 2 | 1.91 | 1.25 | 2.81 | 3.59 | 283 |
| 1-1/4 | 0.88 | 4.44 | 2.22 | 2.34 | 2.17 | 1.44 | 3.13 | 4.13 | 438 |
| 1-3/8 | 0.88 | 4.44 | 2.22 | 2.34 | 2.31 | 1.44 | 3.13 | 4.19 | 442 |
| 1-1/2 | 0.88 | 4.94 | 2.38 | 2.59 | 2.44 | 1.44 | 3.41 | 4.44 | 544 |
| 1-5/8 | 1 | 5.31 | 2.62 | 2.75 | 2.66 | 1.63 | 3.63 | 4.75 | 704 |
| 1-3/4 | 1.13 | 5.75 | 2.75 | 3.06 | 2.92 | 1.81 | 3.81 | 5.24 | 934 |
| 2 | 1.25 | 6.44 | 3 | 3.38 | 3.03 | 2 | 4.44 | 5.88 | 1300 |
| 2-1/4 | 1.25 | 7.13 | 3.19 | 3.88 | 3.19 | 2 | 4.56 | 6.38 | 1600 |
| 2-1/2 | 1.25 | 7.69 | 3.44 | 4.13 | 3.69 | 2 | 4.69 | 6.63 | 1900 |
| 2-3/4 | 1.25 | 8.31 | 3.56 | 4.38 | 4.88 | 2 | 5 | 6.88 | 2300 |
| 3 | 1.5 | 9.19 | 3.88 | 4.75 | 4.44 | 2.38 | 5.31 | 7.61 | 3100 |
| 3-1/2 | 1.5 | 10.75 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 6 | 2.38 | 6.19 | 8.38 | 4000 |
There are also many other standard wire rope clips, such JIS standard wire rope clip, BS462 wire rope clip, simplex wire rope clip, and duplex wire rope clip etc. Contact us for more details.
How do I choose the correct size of a wire rope clip?
To choose the right size of a wire rope clip, you must match it precisely to the diameter of the wire rope being used. The clip size is always based on the rope diameter, not the dimensions of the clip itself.
For example:
- 6 mm rope → use a 6 mm wire rope clip
- 1/2″ rope → use a 1/2″ wire rope clip
What are the spacing and torque requirements when installing wire rope clips?

Proper spacing and torque are critical for the safe and effective use of wire rope clips.
1. Clip Spacing (Installation Interval)
- General rule:
Space the clips at intervals of 6 to 7 times the wire rope diameter.
For example, for a 10 mm wire rope, the clips should be spaced 60–70 mm apart. - This spacing ensures even load distribution along the clamped area.
2. Torque Requirements
- Each wire rope clip must be tightened using a calibrated torque wrench.
- Under-tightening can cause slippage; over-tightening can damage the rope.
What is the correct way to install wire rope clips?
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Wire Rope Clips:
Step 1: Prepare the wire rope
- Measure and bend the wire rope to form the desired loop or eye.
- Make sure the live end (the loaded part) and dead end (the loose tail) are clearly identified.
Step 2: Position the first clip
- Place the first clip one base width from the dead end of the rope.
- Ensure the saddle is on the live end, and the U-bolt is on the dead end. 📌 Remember: “Never saddle a dead horse.”
- Add the remaining clips at equal intervals—approximately 6 to 7 times the rope diameter apart.
- Align all saddles on the same side (live end).
Step 4: Tighten the nuts to the recommended torque
- Use a calibrated torque wrench.
- Refer to the manufacturer’s torque chart based on rope and clip size.
Step 5: Load the assembly
- Apply the initial load to the rope—this helps seat the clips and rope strands.
Step 6: Re-tighten all nuts
- After loading, re-tighten each clip to the specified torque.
- Periodically inspect and re-tighten clips during usage, especially in critical applications.
What’s the difference between forged and malleable wire rope clips?
The key difference between forged and malleable wire rope clips lies in their strength, material, and intended application.
| Feature | Forged Clip | Malleable Clip |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Drop-forged steel | Cast malleable iron |
| Strength | High | Medium to low |
| Suitable for Lifting | Yes (when certified) | No |
| Common Standard | G-450, DIN 1142 | DIN 741 |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Risk of Cracking | Low | Higher |
How often should I inspect wire rope clips?
The frequency depends on the application, load conditions, and environment.
General Inspection Guidelines:
| Application Type | Inspection Frequency |
|---|---|
| Lifting or hoisting | Before each use and weekly |
| Static or tensioning only | At least once a month |
| Harsh environments (e.g. marine, outdoor, corrosive) | Weekly or more frequently |
| After initial installation | Re-tighten after 1st load, then inspect regularly |
Can wire rope clips be reused?
For safety-critical applications, always use new clips.
For non-load-bearing tasks, carefully inspect and test any clip before reuse.
Are there alternatives to wire rope clips?
Yes, of course. Such as Aluminum ferrules, sockets etc.
How long should the dead end be when using wire rope clips?
The dead end should extend at least 6 rope diameters beyond the last clip. This ensures there is enough tail to hold under tension and allows for future re-tightening.
Whether you’re working with lifting, rigging, marine, or structural applications, understanding these clips can prevent costly mistakes and ensure secure, long-lasting connections. Contact our team today to get expert advice and high-quality wire rope clips at competitive prices.


